Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) implementation is a strategic imperative for organizations seeking to modernize their cloud call center infrastructure. As global customer service operations demand omnichannel engagement, operational scalability, and remote readiness, VoIP offers a software-defined alternative to traditional telephony. It supports real-time communication, intelligent routing, and analytics—all while reducing operational costs and enhancing flexibility.
However, VoIP transition introduces several complexities. Downtime risks, compatibility with legacy systems, and workforce training gaps often hinder seamless adoption. These challenges can disrupt workflows unless proactively addressed through infrastructure readiness and structured onboarding.
This guide provides an actionable blueprint for decision-makers to deploy VoIP in cloud call centers without disruption. It outlines 11 implementation steps including infrastructure audits, bandwidth validation, call routing configurations, CRM integration, and compliance testing. Each step is crafted to reduce risk and accelerate deployment.
In addition, the guide includes a practical implementation checklist and a section on post-deployment best practices. These resources help streamline training, ensure system reliability, and maintain regulatory alignment. Executives, IT leads, and operations managers can use this guide as a definitive resource to execute VoIP implementation with precision.
Assess Business Communication Needs

Assessing business communication needs defines the technical scope of a VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) system. It sets capacity thresholds and determines integration prerequisites. This step establishes a baseline for aligning system capabilities with current operational demands. It also supports planning for future scalability.
The process should begin with an audit of existing telephony infrastructure, including analog lines, PBX setups, and legacy VoIP deployments. The audit should document limitations in functionality, reliability, cost performance, and integration with digital platforms.
The communication analysis must quantify inbound and outbound call volumes, concurrency levels, and peak load patterns. It must assess the active agent count and geographic distribution. Map preferred communication channels across customer touchpoints such as voice, email, messaging apps, and social platforms. Then, evaluate requirements for omnichannel routing and CRM synchronization.
Recommended tools include call log analyzers, network monitoring dashboards, CRM usage reports, and forecasting templates. Stakeholders include IT managers, contact center supervisors, business process owners, and compliance leads.
Skipping this phase leads to system underperformance, capacity mismatches, and misaligned features. Common pitfalls include omitting multichannel needs, ignoring compliance constraints, underestimating growth, or selecting incompatible solutions.
Evaluate Current Network Infrastructure
Evaluating network infrastructure establishes bandwidth capacity, performance stability, and hardware compatibility for VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) deployment. This step confirms that IT systems meet throughput and reliability requirements.
The evaluation must measure internet speed, uptime consistency, and resilience under concurrent traffic. VoIP quality depends on limiting latency to ≤150 ms, jitter to ≤30 ms, and packet loss to <1%. It also requires 100 kbps per concurrent call and 1 Mbps per user for multi-service use. Business-grade internet with service-level agreements (SLAs) ensures guaranteed throughput.
The assessment must verify that routers and switches support VoIP protocols and Quality of Service (QoS). Use PoE-compatible devices for combined power and data transmission. Configure firewalls to allow VoIP traffic and apply VPN and encryption for secure routing. Use bandwidth analyzers, latency simulators, and stress tests on wired Ethernet.
Stakeholders include network engineers, IT administrators, and security analysts.
Common pitfalls include misestimating bandwidth, omitting peak-hour testing, disregarding jitter and packet loss, retaining outdated hardware, and blocking VoIP ports through firewalls. Skipping QoS setup, over-relying on Wi-Fi, and neglecting encryption protocols also impair deployment success.
Define Call Routing and Use Cases

Defining call routing and use cases determines the operational flow of incoming and outgoing calls in a VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) environment. This step sets the logic for directing customer inquiries to the most relevant agent with minimal delay.
Routing strategies must align with business goals, agent specialization, customer expectations, and integration capabilities. Use cases include customer support, sales, technical assistance, priority handling, and multilingual queues. Organizations must identify whether they need inbound, outbound, or hybrid workflows and configure routing accordingly.
Routing methods include:
- IVR-based routing: Menu selections direct calls to specific departments.
- Skill-based routing: Agents receive calls based on predefined competencies.
- CRM-integrated routing: Customer profiles route calls to previously engaged agents.
- Priority routing: Urgent or high-value calls go to senior staff.
- Geographic routing: Region-based assignment ensures local language support.
- Availability-based routing: Calls are assigned based on real-time agent status.
- Automated Call Distribution (ACD): Balances workload using queue logic.
Configure routing using IVR editors, CRM connectors, ACD rules, and real-time dashboards. Stakeholders include process architects, support leads, and systems engineers.
Common pitfalls include misconfigured IVRs, call loops, static routing, and poor integration with customer data. These issues increase idle time, resolution delays, and customer dissatisfaction.
Select a VoIP-Compatible Cloud Call Center Platform
Selecting a VoIP-compatible cloud call center platform defines the communication infrastructure for managing distributed operations. This step ensures support for remote access, omnichannel routing, CRM synchronization, analytics, and compliance.
Begin by defining operational requirements. Identify primary use cases such as customer support, sales, or technical service and classify call flows as inbound, outbound, or hybrid. Specify communication channels, user volume, concurrency levels, and metrics like First Call Resolution (FCR), Average Handle Time (AHT), and Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT). Define mobility needs and integration dependencies with existing platforms.
Budget planning must cover licensing, hardware, onboarding, and ongoing support. Evaluate platforms that offer:
- IVR, ACD, and skills-based routing
- Real-time reporting and analytics
- CRM and omnichannel integrations
- Call monitoring and recording
- AI automation and predictive routing
- Mobile apps and softphones
- Encryption and regulatory compliance (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA)
Assess usability, reliability, scalability, and available training. Confirm Quality of Service (QoS) support and tools for monitoring latency, jitter, and packet loss. Prioritize vendors with documented onboarding workflows and contingency protocols.
Common pitfalls include feature misalignment, complex user interfaces, underestimated training needs, and selection of unproven vendors.
Check Internet Bandwidth and Redundancy Options
Checking internet bandwidth and redundancy options verifies network capacity and resilience for VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) operations. This step ensures consistent call quality and high system availability.
Bandwidth must support concurrent VoIP sessions without degradation. Allocate at least 100 kbps (upload/download) per active call. For high user density or multi-application environments, provision additional capacity. Measure latency (≤150 ms), jitter (≤30 ms), and packet loss (<1%) under peak conditions using wired Ethernet for accuracy.
Enable Quality of Service (QoS) to prioritize voice traffic. Use bandwidth analyzers and diagnostic tools to validate network readiness. Stakeholders include IT administrators, network engineers, and VoIP integrators.
Redundancy strategies include dual internet links, automatic failover, and backup power systems. Cloud platforms enhance reliability through distributed data centers and built-in disaster recovery. Define contingency protocols to handle outages and service interruptions.
Common pitfalls include under-provisioning bandwidth, omitting QoS configurations, relying on Wi-Fi as the primary connection, skipping stress testing, or lacking failover infrastructure. These oversights compromise call quality, uptime, and service continuity.
Procure VoIP-Ready Hardware (or Assess BYOD Viability)
Procuring VoIP-ready hardware or evaluating Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) viability defines the endpoint strategy for voice communication. Identifying 11 essential VoIP hardware components helps ensure that the selected devices support compatibility, voice quality, and core user functionality. This step ensures device compatibility, voice quality, and user functionality.
Hardware options include:
- IP Phones: Ethernet-connected desk phones suited for fixed workstations with high call volume.
- Softphones: Software clients installed on computers or mobile devices. Enables BYOD by converting existing devices into VoIP endpoints.
- Analog Terminal Adapters (ATAs): Converts analog phones for VoIP. Select models with echo cancellation for audio clarity.
All configurations require headsets. Use headsets with active noise cancellation (ANC) to reduce background noise. Wireless options enhance mobility and agent efficiency.
Ensure routers, switches, and firewalls support VoIP and apply Quality of Service (QoS) to prioritize call traffic. Use wired Ethernet instead of Wi-Fi to minimize jitter, latency, and packet loss. Stakeholders include IT teams, procurement managers, and support engineers.
The BYOD model reduces hardware costs and shortens deployment but depends on employee internet quality and headset standards. Confirm device compatibility with the VoIP platform and vendor support for configuration.
Common pitfalls include device incompatibility, low-quality headsets, and missing QoS settings. Call stability, secure connections, and hardware alignment define success.
Choose VoIP Providers and SIP Trunking Options
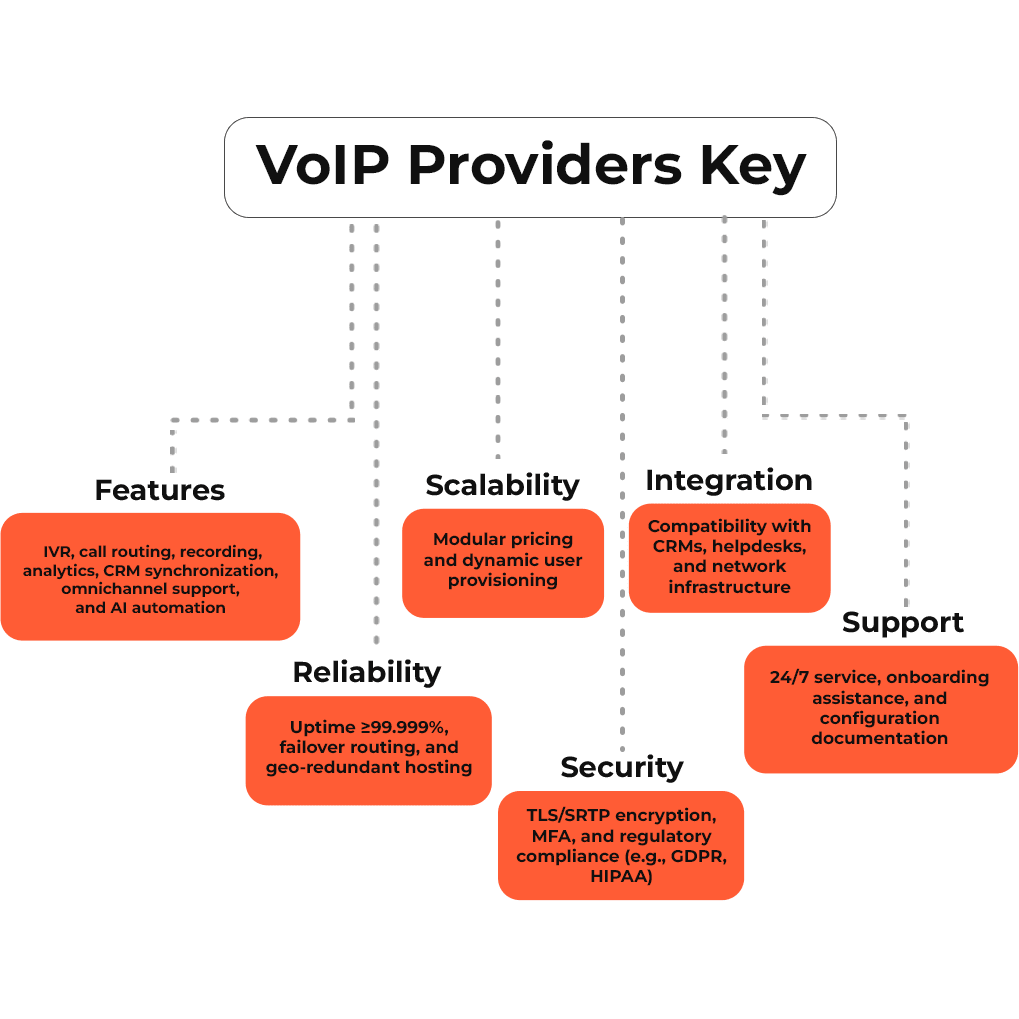
Choosing a VoIP provider and SIP trunking option establishes external call connectivity, routing logic, and protocol compatibility. This step defines system reliability, feature scope, and scalability across communication workflows.
VoIP providers enable number provisioning, SIP-based public network access, and call routing. Select providers based on supported features, uptime guarantees, protocol compatibility, and integration with current systems.
Key selection criteria include:
- Features: IVR, call routing, recording, analytics, CRM synchronization, omnichannel support, and AI automation
- Reliability: Uptime ≥99.999%, failover routing, and geo-redundant hosting
- Scalability: Modular pricing and dynamic user provisioning
- Security: TLS/SRTP encryption, MFA, and regulatory compliance (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA)
- Integration: Compatibility with CRMs, helpdesks, and network infrastructure
- Support: 24/7 service, onboarding assistance, and configuration documentation
Confirm SIP trunking compatibility with VoIP hardware and verify provider support for protocol-level diagnostics. Use trial accounts and benchmarks to assess call quality and system interoperability. Stakeholders include IT leads, procurement managers, operations teams, and compliance officers.
Common pitfalls include mismatched SIP configurations, limited feature sets, poor support, and unclear billing terms. Success depends on seamless SIP integration, consistent connectivity, and verified platform compatibility.
Map CRM and Helpdesk Integrations
Mapping CRM and helpdesk integrations enables synchronized workflows, real-time data visibility, and contextual call management in VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) environments. This step improves agent responsiveness, automates recordkeeping, and personalizes customer interactions.
VoIP systems must interface with CRM platforms such as Salesforce, HubSpot, Zoho, Microsoft Dynamics, and Pipedrive, as well as helpdesk tools including Zendesk, Freshdesk, Intercom, and SAP. Integrations with messaging platforms (e.g., WhatsApp), data tools (e.g., Google Sheets), and vertical systems (e.g., EHRs, inventory software) consolidate communications across customer touchpoints.
Configuration requires API-based or plugin-enabled connectivity. Settings must include field mapping, secure authentication, and synchronization intervals. Middleware may be used where native support is lacking. Conduct functional tests using staging environments to validate system behavior and ensure session persistence across platforms.
Stakeholders include IT architects, CRM administrators, support operations managers, and vendor integration teams. Their responsibilities span system compatibility audits, API key management, and user access configuration.
Common integration failures stem from unvalidated field mappings, lack of failover procedures, incompatible legacy systems, or inadequate data sync testing. Success is defined by automatic call logging, CRM data visibility during live sessions, and consistent information flow across support platforms.
Set Up Number Porting and Call Routing Rules
Setting up number porting and configuring call routing rules secures continuity of business identifiers and establishes intelligent inbound traffic distribution in VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) environments.
Number Porting transfers existing business phone numbers from legacy or alternate VoIP carriers to the new provider. Submit porting requests to the destination provider with supporting documentation. Processing typically spans several days to weeks depending on jurisdiction and provider responsiveness. Plan transitional measures, including temporary routing numbers or Bring Your Own Carrier (BYOC) configurations, to avoid service interruption. Stakeholders include telecom administrators, compliance leads, and vendor liaisons.
Call Routing Rules direct inbound calls based on predefined logic to optimize response accuracy, speed, and customer satisfaction. VoIP platforms support Interactive Voice Response (IVR), skill-based routing, priority routing, CRM-integrated smart routing, geographic distribution, and AI-driven predictive logic. Configuration requires access to the call flow builder or rule engine within the provider’s admin interface. Settings must include fallback handling, agent availability status mapping, and escalation paths.
Route validation requires simulated inbound traffic under load conditions. Stakeholders include operations managers, routing architects, and team supervisors. Common pitfalls include inadequate fallback paths, misaligned skills-tag mapping, or static logic that ignores real-time availability. Success is defined by minimized call wait times, accurate first-contact resolution, and consistent routing performance during peak volumes.
Train Your Agents and Supervisors on New Tools
Training ensures that agents and supervisors use VoIP systems effectively, accelerating adoption and minimizing disruption. This step aligns platform capabilities with user proficiency to sustain operational performance.
Start with a structured training needs assessment based on agent experience—novice, intermediate, and advanced. Novices need platform basics and call handling. Intermediate users require CRM integration and routing workflows. Advanced users and supervisors must understand analytics, live monitoring, and workforce management. Stakeholders include agents, team leads, trainers, quality analysts, and managers.
Training must cover platform navigation, softphone usage, call routing, escalation paths, and security compliance. Use a blended approach combining live sessions, recorded tutorials, guided simulations, and embedded help tools. Vendor-provided training and pilot rollouts with feedback loops improve retention and reduce errors.
Training effectiveness is measured by Net Promoter Score (NPS), call efficiency, handle time, resolution rates, and system adoption metrics.
Common pitfalls include insufficient role-based training, excessive reliance on generic materials, unverified training outcomes, and lack of post-training performance tracking. These gaps lead to misuse, lower productivity, and suboptimal customer experiences. Success depends on targeted instruction, feedback integration, and continuous performance monitoring.
Test Call Quality, Failover, and Compliance Before Launch
Pre-launch testing verifies that the VoIP system meets performance benchmarks, sustains operational continuity, and complies with data protection regulations. This step reduces post-deployment risks by ensuring call clarity, system reliability, and legal conformity.
Call quality must be tested under peak network load. Key metrics include latency below 150 ms, jitter under 30 ms, and packet loss below 1%. Use controlled internal and external calls to validate results. Long-duration tests detect session drops and firewall issues. Apply wired Ethernet and enforce Quality of Service (QoS) for stable transmission. Network engineers and QA personnel conduct diagnostic evaluations.
Validate failover by simulating primary link outages. Confirm seamless switchover to backup internet, power redundancy, and cloud-based disaster recovery. IT administrators and continuity planners must document recovery timelines and system behavior.
Verify security and compliance through penetration tests, configuration reviews, and audit trails. Ensure encryption, firewall rules, intrusion detection, multi-factor authentication, and endpoint protection are active. Compliance officers confirm adherence to GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, or local frameworks.
Common pitfalls include skipping peak-load tests, failing to validate failover, using outdated firmware, misconfigured firewalls, or unenforced encryption. Success depends on full test coverage, contingency documentation, and verified compliance before deployment.
VoIP Implementation Checklist for Cloud Call Centers

- Audit current telephony infrastructure and document capacity thresholds.
- Validate internet bandwidth (≥100 kbps per call) and wired connectivity.
- Ensure latency ≤150 ms, jitter ≤30 ms, and packet loss <1%.
- Confirm router/firewall compatibility with VoIP and configure QoS.
- Conduct stress tests under peak load using Ethernet connections.
- Shortlist VoIP providers with ≥99.999% uptime, SIP support, and SLA-backed reliability.
- Match features to business use cases (IVR, CRM sync, analytics, mobile apps).
- Validate regulatory compliance (GDPR, HIPAA) and encryption standards.
- Confirm 24/7 support availability and onboarding capabilities.
- Evaluate pricing transparency, scalability, and integration APIs.
- Procure IP phones, softphones, ATAs, and ANC headsets.
- Assess BYOD readiness and enforce device compatibility with the VoIP platform.
- Validate compatibility with CRM, helpdesk, and third-party tools.
- Map data fields, test API connections, and conduct session persistence checks.
- Configure routing rules (IVR, skill-based, predictive) and port business numbers.
- Segment users by skill level: novice, intermediate, advanced.
- Train agents on platform navigation, call handling, escalation flows, and CRM use.
- Equip supervisors with tools for live monitoring, analytics, and team management.
- Leverage blended training formats: live sessions, videos, simulations, vendor resources.
- Use performance benchmarks: NPS, call efficiency, resolution time, and adoption metrics.
- Test call quality internally and externally across durations and peak conditions.
- Simulate failover scenarios with dual internet paths and power backups.
- Conduct security audits: enforce encryption, MFA, firewalls, and endpoint protections.
- Pilot test with a user group and validate system readiness.
- Document compliance (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) and create contingency response plans
What are the most common mistakes businesses make during VoIP rollout?
- Skipping Bandwidth Calculations: Failing to calculate per-call bandwidth requirements (minimum 100 kbps per call) can cause jitter, packet loss, and call degradation under load.
- Remedy: Conduct a network capacity assessment using real-time traffic simulation tools. Enforce QoS policies prioritizing RTP streams.
- Improper SIP Trunk Provisioning: Underestimating trunk channel capacity or misconfiguring SIP headers disrupts external connectivity and call delivery.
- Remedy: Dimension SIP trunks for peak concurrent calls. Ensure SIP header integrity and compatibility with the Session Border Controller (SBC).
- Inadequate Codec and NAT Traversal Settings: Using high-bandwidth codecs (e.g., G.711) in constrained networks or failing to configure STUN/TURN/ICE for NAT traversal results in one-way audio or dropped calls.
- Remedy: Optimize codecs for network conditions (e.g., use G.729 where bandwidth is limited). Enable NAT traversal mechanisms in SIP endpoints and firewalls.
- Poor Integration with CRM and Helpdesk Systems: Neglecting to pre-test APIs, middleware, or plugin-based CRM integrations causes data silos and agent inefficiency.
- Remedy: Use sandbox environments to validate CRM field mappings and ensure session persistence across platforms.
- Neglecting End-User Training and Change Management: Assuming intuitive usage leads to resistance or misuse of features like call transfer, analytics, or live monitoring.
- Remedy: Segment training by agent proficiency levels. Include softphone walkthroughs, use-case-based simulations, and system adoption metrics.
- Security and Compliance Gaps: Failing to enforce encryption (TLS/SRTP), firewall rules, or MFA introduces risks like toll fraud, spoofing, and regulatory non-compliance.
- Remedy: Conduct VoIP-specific penetration tests, enable full-path encryption, and audit system access logs.
- No Redundancy or Failover Planning: Lacking secondary ISPs, power backups, or DNS-based failover exposes systems to outages.
- Remedy: Deploy redundant links, UPS systems, and automatic DNS failover policies for continuity.
- Overlooking PSTN Gateway and Legacy Integration: Ignoring PSTN access via SIP-PSTN gateways can disrupt communications with analog systems or external numbers.
- Remedy: Validate gateway provisioning and interworking settings for PSTN compatibility.
- Ignoring Codec Mismatch and Media Negotiation Issues: Endpoint and trunk mismatches on codec negotiation cause failed call setups.
- Remedy: Standardize codec configurations across devices and trunks. Use SBCs to mediate codec translation.
- Lack of Ongoing Monitoring and Firmware Updates: VoIP systems degrade over time without performance analytics, firmware patches, or service reviews.
Remedy: Schedule recurring diagnostics, monitor KPIs (e.g., MOS score, call completion rate), and maintain vendor SLAs.
How can VoIPTech Solutions help make your VoIP implementation faster and easier?
VoIPTech Solutions simplifies VoIP deployment through SIP provisioning, network readiness, CRM integration, and structured onboarding. Our team ensures compatibility with your infrastructure, configures intelligent call routing, and enforces compliance standards like GDPR and HIPAA.
We streamline migration with SLA-backed SIP trunks, seamless CRM/helpdesk integrations, and tailored agent training. Built-in diagnostics and onboarding support minimize downtime and accelerate adoption.
Start with a free consultation, download our migration checklist, or book a platform demo to get started.







