Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) is a communication technology that transmits voice calls over Internet networks instead of using traditional circuit-switched telephone lines. It converts analog voice signals into digital packets for transmission through IP-based systems.
VoIP has emerged as a widely adopted alternative to legacy telephony in modern enterprises. Traditional phone systems are costly to maintain, limited in scalability, and restricted to fixed physical infrastructure. VoIP addresses these limitations by enabling location-independent communication, reducing operational costs, and simplifying system management.
This guide outlines the benefits of VoIP for businesses, its role in modernizing communication infrastructure, and key factors to consider during implementation. Business and IT leaders will gain clarity on how VoIP supports flexibility, remote collaboration, and seamless integration with digital platforms.
How does VoIP work as a communication technology?
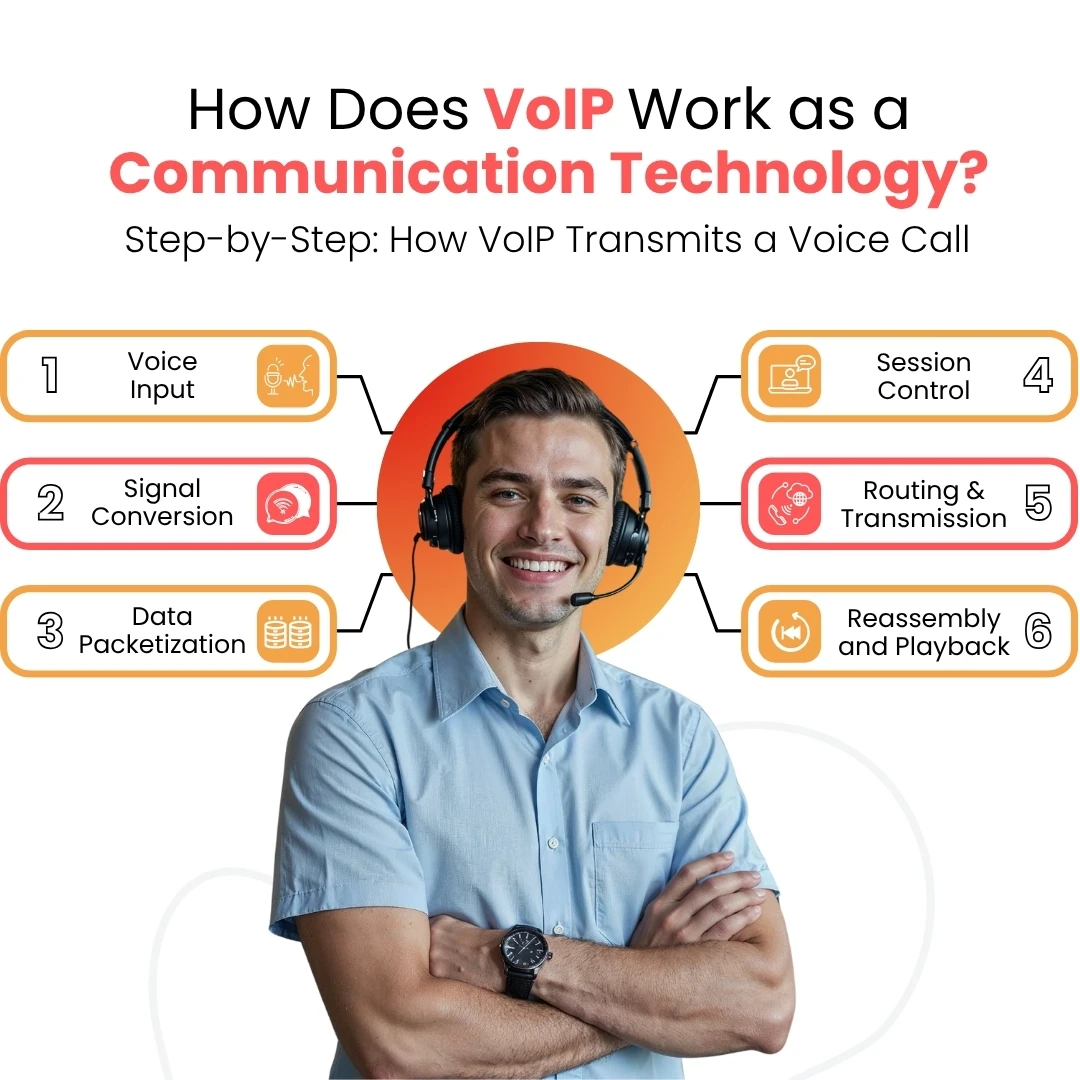
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) is a communication technology that transmits voice as digital data over the Internet. Unlike traditional phone systems, VoIP does not rely on circuit-switched infrastructure. Instead, it enables real-time voice transmission using Internet protocols.
Step-by-Step: How VoIP Transmits a Voice Call
- Voice Input: The user's voice is captured via a microphone or device-integrated input.
- Signal Conversion: A coder-decoder (Codec) compresses and converts the analog voice into digital data.
- Data Packetization: The digital voice data is segmented into smaller data packets.
- Session Control: A signalling protocol, typically Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), initiates, maintains, and terminates the communication session.
- Routing and Transmission: The data packets travel through routers and switches across either the public Internet or a private intranet, depending on the system configuration.
- Reassembly and Playback: The packets are reassembled at the receiver’s end, decoded by the codec, and converted back into audible sound.
What are the components and infrastructure required for VoIP?

Implementing a VoIP system involves a combination of essential hardware, software, and network infrastructure. To achieve optimal performance, businesses should follow these 11 steps for VoIP implementation process. Proper implementation requires aligning these components through a structured approach that addresses technical setup, configuration, and operational readiness.
Essential VoIP Components
- IP Phones: Internet-enabled phones that transmit voice data directly over IP networks.
- VoIP Gateways: Devices that convert analog voice signals into digital packets and vice versa, enabling interoperability with legacy systems.
- Private Branch Exchange (PBX): On-premise or virtual systems that handle call routing, voicemail, and internal communication features.
- Routers and Switches: Network hardware that directs and prioritizes voice data across the internal network.
- High-Speed Internet Connection: A reliable broadband connection is essential for maintaining call quality and service availability.
- SIP Trunking: A method of delivering voice over IP using the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) to connect with the public telephone network.
Cloud-Based Alternatives

- Hosted PBX: A cloud-managed phone system that eliminates the need for on-site PBX hardware, offering easy scalability and lower maintenance.
- Unified Communications as a Service (UCaaS): A comprehensive cloud-based platform combining VoIP with messaging, video conferencing, and collaboration tools.
- Cloud-Based Softphones: Software-based phone applications that operate on computers and mobile devices, enabling VoIP communication without physical handsets.
- VoIP-as-a-Service Providers: End-to-end solutions offered by third-party vendors that manage infrastructure, SIP services, analytics, and integration with business applications.
These components and services provide businesses with flexible deployment options. Organizations can choose a fully on-premise system, migrate to the cloud, or adopt a hybrid approach.
How Do VoIP Phone Systems Differ from Traditional Landline Systems?
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) and traditional landline systems (Public Switched Telephone Network-PSTN) operate on fundamentally different technologies. While landline phones rely on circuit-switched telephony using copper wires, VoIP transmits voice data over internet protocols, leveraging digital networks. This distinction leads to measurable differences in cost, flexibility, scalability, and infrastructure requirements.
Key Differences Between VoIP and Traditional Landline Systems
|
Feature |
VoIP Systems |
Traditional Landline Systems (PSTN) |
|---|---|---|
|
Technology Base |
Uses internet protocol and packet-switched networks |
Uses circuit-switched copper-based networks |
|
Cost |
Lower operational and long-distance calling costs |
Higher maintenance and call charges |
|
Flexibility |
Operates from any internet-enabled device/location |
Fixed to specific physical infrastructure |
|
Scalability |
Easily scalable via cloud or network upgrades |
Adding lines requires hardware and wiring |
|
Hardware |
Requires IP phones, routers, and internet access |
Requires analog phones, telephone jacks, and exchange equipment |
|
Maintenance |
Managed via software updates and cloud services |
Requires physical repairs and periodic technician visits |
|
Integration |
Seamlessly integrates with CRMs, analytics tools, and communication platforms |
Limited integration capabilities |
Businesses choosing VoIP gain modern communication capabilities with improved cost control, dynamic usage, and integration into broader digital ecosystems. Traditional landlines provide consistent performance but offer limited scalability and may result in higher long-term costs.
What are the business benefits of adopting VoIP solutions?
VoIP solutions offer businesses a modern and strategic communication advantage. By replacing traditional telephony with internet-based calling, companies unlock a range of operational, financial, and technical benefits.
Key Benefits of VoIP for Businesses
- Significant Cost Savings
- VoIP reduces long-distance call charges and infrastructure costs by using internet bandwidth instead of analog lines.
- Scenario: A startup with limited capital uses VoIP to connect global clients at minimal call rates, avoiding the need for costly PBX hardware.
- Remote Work Enablement
- VoIP supports location-independent communication, allowing employees to make and receive calls from anywhere via softphones or mobile apps.
- Scenario: A digital marketing agency equips its remote team with softphone access, ensuring seamless client interactions across time zones.
- Scalability and Flexibility
- Businesses can add or remove lines, extensions, and features without major hardware changes, making VoIP ideal for growing organizations.
- Scenario: A call center rapidly scales its agent capacity during peak campaign seasons using cloud-based VoIP without physical setup delays.
- Unified Communications
- VoIP integrates with CRMs, video conferencing, chat, voicemail-to-email, and analytics tools to centralize communication functions.
- Scenario: A mid-sized enterprise connects VoIP with their CRM to log call activity automatically, improving sales and customer service efficiency.
- Business Continuity
- During outages or office closures, VoIP systems reroute calls or enable access via alternate devices to ensure uninterrupted communication.
- Scenario: During a natural disaster, a regional service firm reroutes inbound support calls to mobile devices using VoIP’s auto-failover feature.
What types of VoIP services are available for businesses?
VoIP services can be categorized in several ways based on deployment models, connection types, and technology used. These categories allow businesses to match VoIP services to their communication requirements, IT environment, and scalability objectives. Below is a comprehensive breakdown of the most common VoIP service types:

In-House VoIP Systems
- Hosted and managed entirely within the organization’s infrastructure.
- Requires on-site PBX servers, IP phones, and dedicated IT resources.
- Offers full control and customization.
- Best suited for large enterprises with regulatory or security concerns.
Hosted VoIP Systems (Cloud VoIP)
- Provided by third-party vendors such as RingCentral, Ooma, or Nextiva.
- No need for on-premise servers.Only internet and IP devices required.
- Cost-effective, scalable, and ideal for startups and SMEs.
- Quick setup and minimal maintenance.
Hybrid VoIP Systems
- Combines in-house hardware with cloud-based VoIP services.
- Offers flexibility and redundancy.
- A great choice for businesses transitioning from legacy systems or requiring customized configurations.
SIP Trunking
- Bridges your on-premise PBX system with the internet.
- Replaces traditional phone lines with virtual lines via the internet.
- Enables businesses to retain existing hardware while gaining VoIP benefits.
- Highly scalable and cost-efficient for organizations with heavy call volumes.
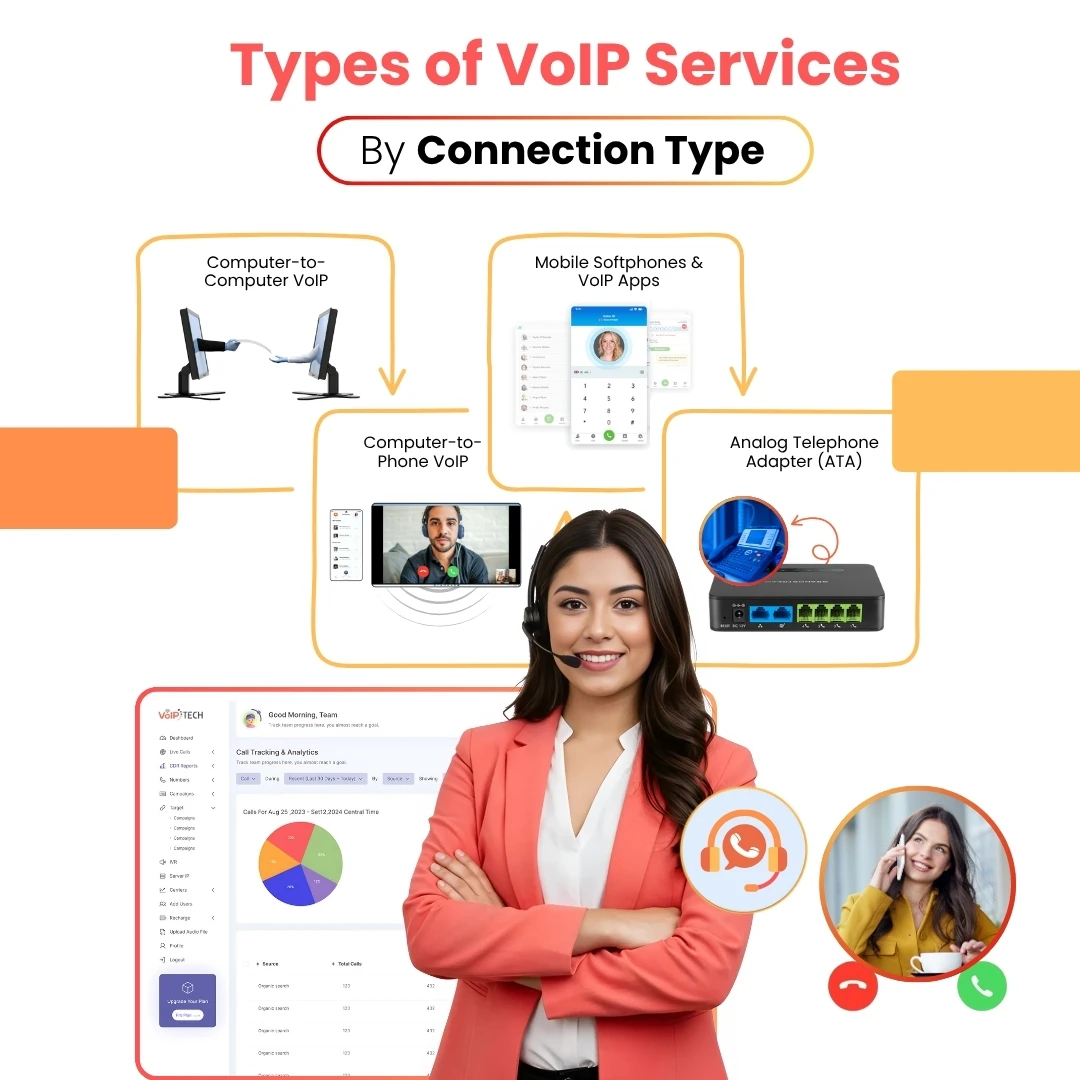
Computer-to-Computer VoIP
- Free internet-based calls between users on the same platform (e.g., Zoom, Skype).
- Requires only VoIP software. No hardware investment.
- Ideal for internal team collaboration or remote teams.
Computer-to-Phone VoIP
- Allows users to call landlines or mobile numbers from a PC or laptop.
- Often requires a VoIP service provider and may involve call charges.
- Useful for customer-facing teams and support centers.
Mobile Softphones & VoIP Apps
- Apps like WhatsApp, Zoiper, Google Voice, or Bria turn smartphones into VoIP-enabled devices.
- Great for field workers, sales teams, or remote employees.
- Ensures business continuity on the go.
Analog Telephone Adapter (ATA)
- Converts traditional analog phones for VoIP use.
- Ideal for businesses that want to continue using legacy phone equipment.
- Simple, affordable solution for gradual VoIP transition.
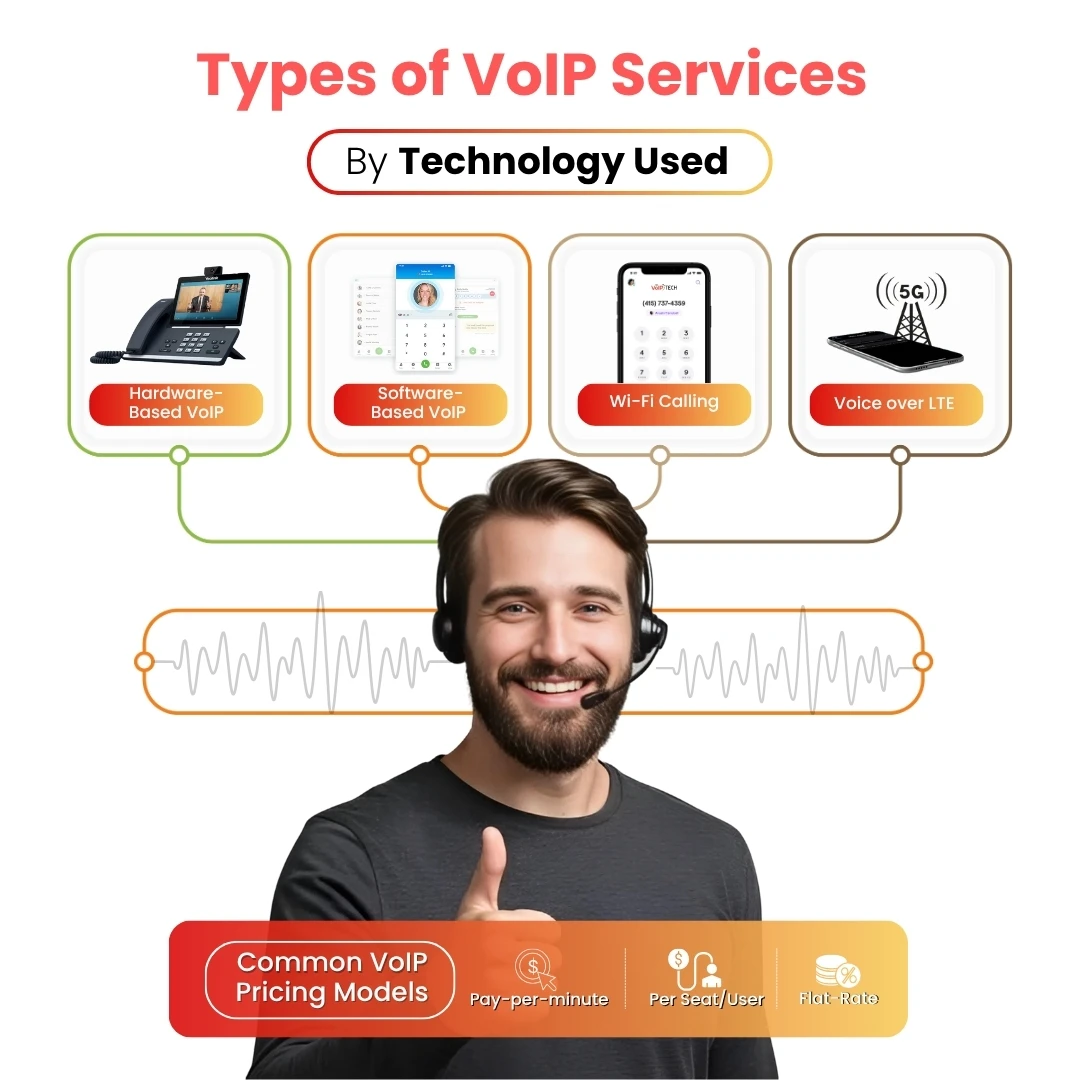
Hardware-Based VoIP
- Involves physical IP phones, routers, or conference phones connected via internet.
- Best for office-based teams with stable infrastructure.
- Offers call clarity and reliability in professional environments.
Software-Based VoIP (Softphones)
- Voice calls through apps on computers or mobile devices. No special equipment needed.
- Examples: Skype, MS Teams, Zoom, and other web-based calling platforms.
- Lightweight and accessible solution.
Wi-Fi Calling
- Built-in mobile OS feature for making calls over Wi-Fi instead of cellular networks.
- Effective in areas with poor cellular coverage.
- Enhances reach without needing a dedicated VoIP app.
Voice over LTE (VoLTE) / Voice over 5G (Vo5G)
- Uses advanced mobile data networks to deliver high-quality calls.
- Carrier-grade reliability and seamless connectivity.
- Increasingly common for enterprise-level mobile communications.
Common VoIP Pricing Models
- Pay-per-minute: Charged based on call duration, ideal for low-volume users.
- Per seat/user: Fixed monthly rate per user, great for growing teams.
- Flat-rate: Unlimited calling with predictable costs, best for high-usage businesses.
How secure and reliable is VoIP for enterprise communication?
VoIP is now widely used in business communication. However, as an internet-based system, it requires careful consideration of security and reliability. Enterprises must evaluate potential risks and corresponding safeguards to maintain uninterrupted communication and data integrity.
- End-to-End Encryption (SRTP)
Secure Real-time Transport Protocol (SRTP) encrypts voice data during transmission, preventing eavesdropping or unauthorized access. It is essential for protecting sensitive business conversations. - Secure SIP (SIPS)
Using Transport Layer Security (TLS) for SIP signaling helps shield call setup data from interception or tampering. - Access Controls & Authentication
Strong password policies, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and user role management reduce unauthorized access risks. - DDoS Mitigation
VoIP systems are vulnerable to Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. Firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and geo-fencing help protect infrastructure.
- Redundancy & Failover Systems
Enterprise-grade VoIP setups include backup servers, alternate call routes, and automatic failover mechanisms to maintain service during outages or hardware failures. - Quality of Service (QoS)
QoS settings prioritize VoIP traffic over the network, reducing latency, jitter, and packet loss. This ensures crystal-clear call quality even during peak data usage. - Network Monitoring
Real-time analytics detect anomalies, monitor call quality, and trigger alerts to prevent service interruptions.
Best Practices for Uptime & Data Safety
- Select a VoIP provider offering service-level agreements (SLAs) that commit to at least 99.9% uptime.
- Regularly update firmware and software to patch vulnerabilities.
- Implement call encryption and secure backups.
- Train staff on security hygiene (e.g., avoiding phishing, using VPNs remotely).
- Conduct regular audits and penetration tests.
When implemented with proper safeguards, VoIP can offer both robust security and enterprise-grade reliability, making it a smart choice for modern business communication.
What regulatory and legal issues apply to VoIP services?
VoIP services are subject to various legal and compliance obligations depending on the country or region in which they are used. These regulations cover everything from emergency calling capabilities to data protection and call recording. Below is a categorized overview of the key compliance requirements:
1. United States
- E911 Compliance
VoIP providers must support Enhanced 911 (E911), allowing emergency services to receive caller location and callback information.
Example: The FCC mandates that VoIP services provide E911 access with location and callback functionality. - Call Recording Laws
Varies by state: - One-party consent states allow recording if one participant is aware.
- Two-party consent states require all participants’ approval.
Businesses must notify or obtain consent based on jurisdiction. - FCC (Federal Communications Commission) Rules
VoIP providers must comply with telecommunications consumer protections, porting rules, and accessibility standards.
2.European Union
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
VoIP services must ensure data protection, encryption, and proper consent for storing or processing personal communication data.
Example: Under GDPR, recording a customer call requires explicit opt-in or documented consent from the individual. - ePrivacy Directive
Regulates the confidentiality of communications, including VoIP, and mandates secure handling of metadata and content.
3.India
- TRAI (Telecom Regulatory Authority of India) Guidelines
- VoIP providers must obtain Unified License or ISP license.
- Internet telephony cannot bypass interconnection charges or illegally terminate international calls.
- Emergency Services
VoIP services in India must offer access to emergency numbers (e.g., 112) if integrated with PSTN. - Call Recording
Recording calls without user consent may violate legal requirements and result in penalties.
4.Other Global Considerations
- Data Sovereignty
Some countries (e.g., Canada, Australia, Germany) require VoIP data to be stored within national borders. - Lawful Interception
Most jurisdictions require VoIP providers to enable lawful interception by government agencies under court orders. - International Call Routing Restrictions
Some nations ban or heavily regulate VoIP for international calls to protect local telecom revenues.
Best Practices for Compliance
- Always inform users if calls are being recorded verbally or via pre-call messages.
- Use geo-fencing and IP restrictions for country-specific legal compliance.
- Partner with local legal advisors or compliance consultants to stay updated.
- Regularly audit VoIP platforms for encryption, data retention, and opt-in protocols.
What factors should businesses evaluate before switching to VoIP?
Transitioning to VoIP can significantly boost communication efficiency, reduce costs, and support scalability, but only if evaluated and implemented thoughtfully. Business and IT decision-makers should assess the following factors to ensure a smooth and future-ready deployment.
VoIP Readiness Checklist for Decision-Makers
- Network Readiness
- Assess current internet bandwidth and reliability.
- Conduct a VoIP traffic simulation or latency/jitter test.
- Ensure routers/switches support Quality of Service (QoS).
- Cost Structure
- Compare total cost of ownership (TCO) for hosted vs. on-premise systems.
- Account for setup fees, monthly charges, licensing, hardware, and add-ons.
- Evaluate pricing models: per-user, flat-rate, or usage-based.
- User Training & Change Management
- Check vendor support for onboarding and training sessions.
- Plan for internal adoption especially for remote or non-tech-savvy staff.
- Identify required user features (voicemail-to-email, mobile apps, softphones).
- Integration Capabilities
- Ensure compatibility with CRM, helpdesk, and UCaaS platforms.
- API availability for custom workflows or automation.
- Sync with existing PBX or hybrid setups (if applicable).
- Security & Compliance
- Check for SRTP/TLS encryption support.
- Ask about DDoS protection, firewall compatibility, and intrusion detection.
- Ensure vendor compliance with local/global regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, TRAI).
- Vendor Support & SLA
- 24/7 technical support availability (chat, phone, email).
- Uptime guarantees and redundancy/failover architecture.
- Local support options (important for region-specific troubleshooting).
Hosted vs. On-Premise: Deployment Trade-Offs
|
Feature |
Hosted VoIP |
On-Premise VoIP |
|---|---|---|
|
Setup Cost |
Low (subscription-based) |
High (hardware, licenses) |
|
Scalability |
Easily scalable |
Complex and hardware-dependent |
|
Maintenance |
Handled by vendor |
Requires in-house IT |
|
Customization |
Limited to vendor’s offerings |
Full control and customization |
|
Security Control |
Relies on vendor protocols |
Full internal security control |
Decision Matrix: Why Choose VoIP?
|
Need/Goal |
VoIP Benefit |
|---|---|
|
Reduce communication costs |
No long-distance fees; flat-rate options |
|
Enable hybrid/remote work |
Mobile and softphone access |
|
Integrate with modern tools |
CRM, ticketing, and workflow integrations |
|
Support business growth |
Scalable user and location expansion |
|
Modernize legacy infrastructure |
IP-based flexibility, no copper wire dependence |
|
Ensure business continuity |
Geo-redundancy and failover systems |
Switching to VoIP is not just a tech upgrade but it's a strategic shift. Evaluate your current communication pain points and map them against VoIP's advantages to ensure your investment delivers maximum ROI.
What are the common challenges businesses face when adopting VoIP?
While VoIP offers immense advantages, businesses may encounter technical, operational, and adoption-related hurdles during implementation. Understanding these challenges in advance helps ensure a smoother transition.
Key Challenges in VoIP Adoption (and How to Mitigate Them)
- Internet Dependency & Bandwidth Limitations
- VoIP heavily relies on a stable internet connection.
- Insufficient bandwidth can result in poor call quality or dropped connections.
- Mitigation: Conduct a network assessment and allocate dedicated bandwidth for VoIP using QoS (Quality of Service) settings.
- Call Quality Issues (Latency, Jitter, Packet Loss)
- Delays in audio (latency), voice distortion (jitter), or missing data packets degrade the user experience.
- Mitigation: Use enterprise-grade routers, prioritize voice traffic via QoS, and partner with a VoIP provider that offers regional servers and redundancy.
- E911 Emergency Service Limitations
- Unlike traditional phone lines, VoIP calls may not automatically transmit accurate location data during emergencies.
- Mitigation: Register each VoIP line with a valid physical address (Enhanced 911 service), and educate employees about using emergency calling features.
- Security Threats (DDoS, Call Interception, VoIP Fraud)
- VoIP systems are susceptible to cyberattacks like denial-of-service, call spoofing, or unauthorized access.
- Mitigation: Implement SRTP and TLS encryption, enable firewalls and intrusion detection, and choose vendors with proven DDoS protection mechanisms.
- Resistance to Change or Inadequate Staff Training
- Employees may be hesitant to adopt new systems or may lack training in using VoIP interfaces and features.
- Mitigation: Offer onboarding sessions, create user-friendly guides, and involve employees in testing and feedback phases.
Example Scenario:
A midsize call center upgraded to a cloud-based VoIP solution but experienced jitter and echo during high-traffic hours. After conducting a bandwidth test, they discovered insufficient upload capacity. The issue was resolved by upgrading to a higher-speed internet plan and setting QoS rules to prioritize voice packets.
What are the differences between VoIP and IP telephony?
Though often used interchangeably, Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) and IP Telephony are not exactly the same. Understanding the subtle differences helps businesses make more informed technology decisions.
Definition and Scope
- Voice over Internet Protocol(VoIP):
- Refers specifically to the technology that transmits voice data over IP networks like the internet.
- Focused on voice communication, such as calls made via Skype, Zoom, or WhatsApp.
- Used in both consumer apps and business systems.
- IP Telephony:
- A broader term that includes VoIP, but also encompasses fax, voicemail, video conferencing, instant messaging, and unified communications delivered over IP networks.
- Typically used in enterprise and telecom industry contexts when referring to the entire digital communication infrastructure, not just voice.
Key Differences at a Glance
|
Aspect |
VoIP |
IP Telephony |
|---|---|---|
|
Scope |
Voice-only communication |
Voice + other media over IP |
|
Usage Context |
Often consumer-level or SMB apps |
Enterprise-grade communications |
|
Functionality |
Calling, voicemail |
Calling, conferencing, messaging |
|
Typical Users |
General public, small businesses |
IT teams, telecom providers, ISPs |
|
Example Tools |
WhatsApp, Google Voice, Skype |
Unified Communications Platforms, SIP-based PBX systems |
When to Use Each Term
- Use VoIP when referring strictly to voice calling over the internet.
- Use IP Telephony when discussing integrated communications solutions in corporate environments or telecom architectures.
VoIP is a subset of IP telephony. If your business is simply making calls online, you're using VoIP. If you're managing a full suite of IP-based communication tools, you’re operating within the realm of IP telephony.
How do VoIP numbers work and what are their use cases?
A VoIP number is a virtual phone number assigned to a user or device, enabling voice communication over the internet instead of traditional telephone lines. Unlike landline numbers tied to a specific location, VoIP numbers are location-independent, portable, and globally accessible.
How VoIP Numbers Differ from Traditional Phone Numbers
|
Feature |
Traditional Numbers |
VoIP Numbers |
|---|---|---|
|
Location Dependency |
Tied to a physical line or address |
Can be used from any internet connection |
|
Portability |
Limited |
High – Easily moved between devices/locations |
|
Device Flexibility |
Requires landline/mobile hardware |
Works on phones, laptops, tablets, softphones |
|
Area Codes |
Based on physical location |
Can choose any area code (virtual presence) |
|
Cost |
Higher due to hardware/line costs |
Typically lower; uses internet data |
Key Features of VoIP Numbers
- Number Portability: Users can keep the same number when switching service providers or devices.
- Virtual Area Codes: Businesses can choose numbers with area codes from regions where they want to establish a local presence regardless of their actual location.
- Multi-device Access: One VoIP number can ring on multiple devices simultaneously or in sequence.
- Call Forwarding & Routing: Calls can be easily forwarded to any device or location without changing the number.
- Global Accessibility: Ideal for international teams and remote workers.
Common Use Cases for VoIP Numbers
- Customer Support Lines:
Set up toll-free or local virtual numbers for customer service, support desks, or help centers. - Remote & Hybrid Teams:
Employees working from home or on the go can receive and make business calls on any internet-connected device. - Call Centers:
VoIP numbers allow call centers to operate virtually, reduce infrastructure costs, and scale quickly. - International Business Presence:
Companies can establish virtual offices in other countries by using local VoIP numbers with matching area codes. - Freelancers & Consultants:
Professionals can maintain a dedicated work number without needing a separate physical line.
What are common examples of VoIP applications and platforms?
VoIP applications enable voice and multimedia communication in both personal and professional environments. From casual calls to enterprise-grade unified communication, VoIP platforms cater to a wide range of needs. Below is a categorized list of popular VoIP apps, separated by consumer and business use.
Consumer-Focused VoIP Applications
|
Platform |
Key Features |
Pricing Tier |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Voice/video calls, messaging, end-to-end encryption |
Free |
|
Skype |
Voice/video calls, group chat, international calling |
Free; paid for PSTN calls |
|
Google Voice |
Call forwarding, voicemail, call screening, number porting |
Free (basic), Paid (business) |
|
Zoom (Free) |
Personal meetings, limited-duration calls |
Free; Paid upgrades |
|
Viber |
Voice/video chat, file sharing, Viber Out for external calls |
Free; Viber Out credits |
Business-Oriented VoIP Platforms
|
Platform |
Best For |
Core Features |
Pricing (Starting) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Zoom (Business) |
Video conferencing + VoIP |
HD video/audio meetings, phone system, team chat |
$14.99/user/month |
|
RingCentral |
Full UCaaS solution |
VoIP calling, messaging, video, integrations with CRM, analytics |
$20/user/month |
|
Nextiva |
SMB communications |
Auto-attendant, call routing, CRM integration, VoIP calls, analytics |
$23.95/user/month |
|
Vonage |
Flexibility for SMBs |
Cloud PBX, call forwarding, desktop/mobile apps, integrations |
$19.99/user/month |
|
8x8 |
Global contact centers |
VoIP, video, analytics, call queues, multi-level IVR |
$24/user/month |
|
Microsoft Teams (Phone) |
Microsoft ecosystem users |
VoIP calling, collaboration tools, Office 365 integration |
From $8/user/month add-on |
Summary of Use Cases
- Consumers benefit from free, secure, and easy-to-use apps for everyday communication.
- Businesses rely on scalable, feature-rich platforms that integrate with productivity tools, CRM, and customer support software.
These platforms allow users to make and receive calls on multiple devices, reduce telephony costs, and streamline communication workflows whether at home, in-office, or on the move.
How does VoIP impact remote work and hybrid team collaboration?
VoIP plays a transformative role in enabling modern remote and hybrid work environments by ensuring seamless, location-independent communication.
Key Ways VoIP Supports Remote Teams:
- Mobility & Flexibility: Employees can make and receive business calls from anywhere using VoIP apps on mobile or desktop.
- Video Conferencing: Integrated video and audio conferencing helps teams collaborate in real time.
- Call Forwarding: Automatically routes calls to the appropriate device or person, ensuring no missed conversations.
- Team Messaging: Many VoIP platforms include chat and file-sharing features for daily communication needs.
Benefits for Remote and Hybrid Teams:
- Increased Productivity: Team members stay connected regardless of location, reducing delays and improving turnaround time.
- Geographic Flexibility: VoIP untethers communication from office desks, supporting a global workforce.
- Cost Savings: No expensive hardware or on-premise systems; VoIP cuts telecom bills dramatically.
- Simplified IT: Cloud-based solutions mean updates and maintenance are handled externally.
Real-World Examples:
- Zapier: A fully remote company that relies on VoIP tools like Zoom and Slack for all communications.
- HubSpot: Uses VoIP systems integrated with their CRM to manage hybrid teams across global offices.
- Buffer: Operates remotely with VoIP-powered team meetings, customer support, and internal collaboration.
With VoIP, your team doesn’t need to be in the same building or even the same continent to stay productive and aligned.
How can businesses upgrade to our cloud-based VoIP solution?
Transitioning to a cloud-based VoIP solution isn’t just a technology shift, but it’s a strategic decision that empowers modern businesses to communicate smarter, scale faster, and operate with greater flexibility.
Traditional phone systems come with their own set of pain points: high hardware costs, limited mobility, inconsistent call quality, and complex maintenance needs. Our cloud-based VoIP solution directly addresses these challenges by eliminating hardware overhead, enabling seamless communication across locations, and ensuring crystal-clear voice quality through intelligent routing and bandwidth optimization.
Why Make the Switch?
- Scalability Made Simple: Add or remove users in minutes which is perfect for growing teams or seasonal workforce adjustments.
- High Reliability & Uptime: Geo-redundant infrastructure and failover systems ensure your communication never goes dark.
- Cost Efficiency: No bulky hardware, no surprise maintenance costs. Just predictable and affordable pricing.
- Remote Collaboration Support: Empower hybrid teams with mobile apps, video conferencing, and call forwarding tools.
- Smart Integrations: Seamlessly connect with your existing CRMs, helpdesk software, and workflow automation tools.
Pain Points We Solve:
- No more physical line limitations. You can work from anywhere.
- No need for expensive PBX hardware.
- No IT overload. Our experts handle setup, monitoring, and updates.
Getting Started Is Easy:
We guide you through every step from assessing network readiness to complete onboarding and staff training. Whether you're migrating from PSTN or upgrading your existing VoIP, our team ensures a smooth, disruption-free transition.







